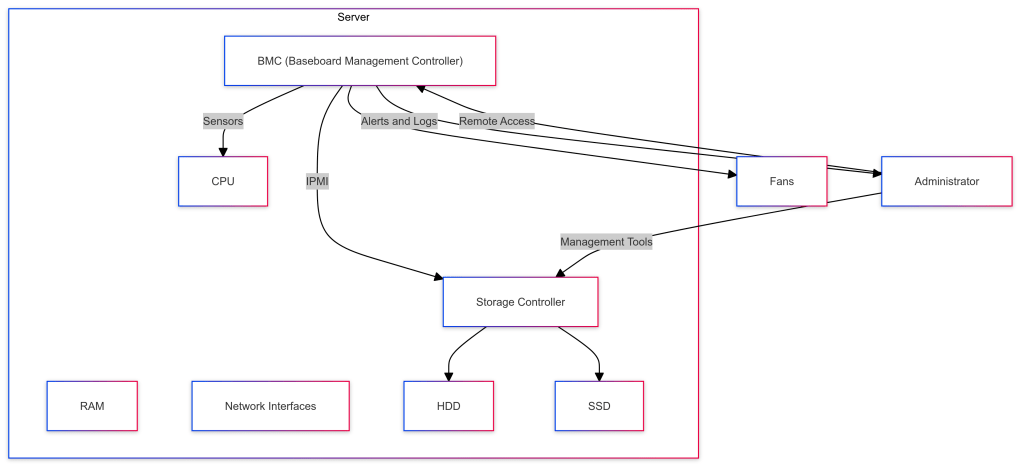
The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) is an embedded system integrated into most server motherboards to manage and monitor the hardware components remotely, independent of the operating system. It is crucial for out-of-band management, allowing administrators to monitor, manage, and diagnose hardware even when the server is off or unresponsive.
BMC Overview
Purpose: Offers out-of-band management capabilities for monitoring and controlling server hardware.Communication: Uses IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) to interact with system components.Features:
- Remote power control (on/off/reset).Hardware monitoring (temperature, voltage, fan speed).Remote console access (KVM over IP).Event logging and alerts.
Controller Storage Overview
Purpose: Manages and controls storage devices like RAID arrays, SSDs, and HDDs.Functions:
- Configures and manages storage arrays.Monitors storage health and performance.Provides redundancy and data protection mechanisms (RAID levels).Facilitates storage provisioning and allocation.
How BMC Works with Controller Storage
BMC interacts with controller storage primarily for monitoring and management purposes. It uses IPMI to communicate with the storage controller, collect health and status information, and facilitate remote management actions.
Initialization and Configuration:
- BMC Initialization: On server power-up, the BMC initializes independently of the main server components and starts monitoring hardware status.Configuration: BMC is configured with a static IP address so that administrators can remotely communicate with it using IPMI.
Health Monitoring and Management:
- Storage Health: BMC communicates with the storage controller to monitor the health and status of the attached storage devices (HDDs, SSDs).IPMI Commands: IPMI commands are sent from the BMC to the storage controller to gather temperature data, drive status, RAID health, and other metrics.
Alerting and Event Logging:
- Event Detection: BMC continuously monitors for hardware events such as drive failures, temperature thresholds being exceeded, or RAID array issues.Alerting: When an issue is detected, BMC logs the event and can send alerts to administrators via SNMP traps, email notifications, or management consoles.Logging: Events are recorded in the System Event Log (SEL), accessible via the BMC interface.
Remote Management Capabilities:
- Power Control: Administrators can use BMC to power cycle the server remotely if needed.Storage Configuration: Using the management interface, admins can reconfigure RAID arrays, replace failed drives, and perform other storage management tasks.Console Access: KVM over IP functionality allows direct interaction with the server’s console for troubleshooting without being physically present.
Example Management ActionsMonitor Storage Health
Access BMC via Web Interface or IPMI Tool:
- Web Interface: Login using BMC’s IP address and admin credentials.IPMI Tool: Use command-line IPMI tools to access BMC.ipmitool -I lanplus -H -U -P sensor
Check Storage Status:
- Use the BMC interface to check the status of storage devices managed by the storage controller.Look for entries related to disk health, RAID array status, and temperature sensors.
Configure RAID Arrays
Login to Storage Controller via BMC:
- Use remote console access provided by BMC to login to the storage controller’s management interface.
Create or Modify RAID Arrays:
- Access the storage configuration utility.Create new RAID arrays or modify existing ones based on storage needs.Monitor the build and synchronization process using BMC.
Alert and Log Management
Set Up Alerts:
- Configure the BMC to send SNMP traps or email alerts when specific events occur (e.g., drive failure, temperature exceeds threshold).Use the web interface or IPMI commands to set up these alerts.
Review Event Logs:
- Access the System Event Log (SEL) via the BMC interface.Use IPMI commands to view logs:ipmitool -I lanplus -H -U -P sel list